
Extract Audio From Video File A Creator's Guide
If you've ever needed to grab the audio from a video file, you've probably used free tools like VLC Media Player or Audacity. It’s a straightforward process: import the video, then export it as an audio-only format like MP3 or WAV. This pulls the entire audio track out, ready for you to use on its own.
But why would you even need to do this?
Why You Need To Extract Audio From Video

Being able to separate audio from video isn't just a neat technical trick; it's a core skill for anyone creating content today. It’s all about repurposing what you’ve already made, seriously boosting its quality, and opening up creative possibilities you might not have considered.
Let’s say you just wrapped up a fantastic interview on a video call, but the connection was terrible and the video is a glitchy mess. No problem. By pulling out just the audio, you can rescue that conversation and turn it into a crisp, clean podcast episode. Just like that, a flawed video becomes a high-quality piece of audio content.
Expanding Your Creative Toolkit
This technique is a go-to for musicians and producers. They often lift unique sounds from live performance videos—a killer drum break, a specific guitar riff, or even the energy of the crowd—and use them as samples in new tracks. Suddenly, every video you've ever recorded becomes a potential sound library.
Video editors also lean on this constantly. Imagine trying to clean up dialogue in a scene with a ton of distracting background noise. By extracting the audio track, an editor can take it into a dedicated audio tool and apply powerful noise reduction or EQ adjustments—something that’s often clunky or impossible to do well inside the video editing software.
The big idea here is simple: your video files are packed with valuable audio. By learning to extract it, you can repurpose, polish, and reuse these assets, getting way more mileage out of the content you worked so hard to create.
The Evolution of Audio Extraction
The growing demand for top-notch audio is clearly reflected in the market. The professional audio market is on track to hit USD 17.82 billion by 2031, largely thanks to the creator economy's insatiable need for better sound tools. You can explore more data on this expanding market to see where things are headed.
In the past, we had to rely on manual tools that could only rip the entire audio track. It worked for basic tasks, but anything more complex was a headache. Now, things have changed completely. AI has entered the scene, allowing creators not just to extract the whole track, but to surgically isolate specific sounds from within a busy mix.
A Look at the Go-To Free Audio Extraction Tools

While advanced AI tools offer incredible precision, sometimes you just need to rip the entire audio track from a video without any fuss. For years, I and countless other creators have relied on a handful of powerful, free programs that get the job done quickly and reliably.
These are the workhorses of audio extraction. They're perfect when you need the whole audio stream—think turning a video interview into a podcast episode or grabbing a song from a music video.
Let's break down three of the most trusted options: FFmpeg, VLC Media Player, and Audacity. Each one fits a different style, whether you're a command-line pro or prefer a visual interface.
The Power User's Choice: FFmpeg
If you're comfortable in a terminal window, FFmpeg is hands-down the fastest and most powerful tool for the job. It’s a command-line utility that media professionals swear by. No graphical interface, just pure, efficient processing that’s perfect for scripting and batch jobs.
To pull an uncompressed, high-quality WAV file from a video named my-video.mp4, this is the command you'd run:ffmpeg -i my-video.mp4 -vn -acodec pcm_s16le audio-output.wav
Need a more web-friendly MP3 instead? The command is just as simple, but gives you control over the final quality.ffmpeg -i my-video.mp4 -vn -ar 44100 -ac 2 -b:a 192k audio-output.mp3
This second one sets the bitrate to a solid 192k, a great balance between file size and quality. It’s my go-to for quick conversions.
The Everyday Tool You Already Have: VLC Media Player
Most people think of VLC as just a media player, but it has a surprisingly capable conversion tool built right in. This is the perfect option if you’d rather click through menus than type commands.
The whole process is tucked away under its 'Convert / Save' feature.
- First, open VLC and head to Media > Convert / Save.
- Add your video file, then click the 'Convert / Save' button again.
- In the new window, look for the 'Profile' dropdown menu. You’ll find ready-made audio profiles like “Audio - MP3” or “Audio - FLAC.”
- Just pick one, choose where to save the file, and hit 'Start.' VLC does the rest. It's that easy.
The Editor's Workflow: Audacity
If you're extracting audio because you plan to edit it immediately, Audacity is your most direct route. It cuts out the middle step of converting the file separately.
You can often just drag your video file and drop it right into the Audacity window. It intelligently strips out the video and imports the audio track as a waveform, ready for you to start trimming, applying effects, or cleaning up noise. Once you’re done, you can export it in any format you need, like WAV or MP3.
The core strength of these classic tools is their reliability for full-track extraction. They are designed to pull the entire audio stream from a video, which is perfect for many common tasks.
To get a better sense of your options, including some browser-based tools, you can explore our guide on online audio extractors.
Comparing Free Audio Extraction Tools
To help you decide which tool fits your needs, here’s a quick breakdown of their strengths and weaknesses.
| Tool | Primary Use | Ease of Use | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| FFmpeg | Fast, command-line conversions and batch processing | Difficult (CLI only) | Requires comfort with the terminal; steep learning curve |
| VLC | Quick, simple conversions with a graphical interface | Easy | Limited control over conversion settings |
| Audacity | Direct import for immediate audio editing and manipulation | Moderate | Can be slow with large video files; not for batch work |
Ultimately, these free tools are powerful allies in any creator's toolkit. Their main limitation, however, is that they can't isolate specific sounds within a track—they take everything. For tasks requiring that level of precision, a different approach is needed.
A Smarter Way to Isolate Sound with AI
The classic tools we’ve covered are brilliant for grabbing an entire audio track from a video. But they all hit the same wall: they can’t tell the difference between the sounds mixed together on that track. If you need more than just the full mix, you need a completely different approach. This is where modern AI tools come in, moving beyond simple extraction and into true sound isolation.
Forget just ripping the whole audio stream. Imagine being able to listen into a recording and pull out just a single sound element. This isn't a futuristic concept anymore; it's exactly what AI-powered tools like Isolate Audio are built to do. These platforms change the game by actually understanding the content of your audio, not just the file it's saved in.
This opens up a whole new world of creative possibilities. You could lift the crisp sound of footsteps on gravel for a foley project, separate a specific backup singer’s harmony from a live band recording, or even pull a roaring stadium crowd away from a commentator's voice.
How AI Hears and Separates Audio
From the outside, the process feels almost like magic. But behind the scenes, it’s all driven by sophisticated machine learning models. For you, the workflow is dead simple.
- Upload Your Video: You start with the video file that has the mixed audio you need to work with.
- Describe What You Want: Instead of wrestling with EQs and filters, you just type what you want to hear. A simple text prompt is all it takes.
- Get Two Tracks Back: The AI gets to work and gives you two clean audio files. One has the exact sound you asked for, and the other has everything else.
This single step can replace hours of painstaking manual editing—the kind of work that used to require deep knowledge of phase cancellation, spectral editing, and intricate filtering.
The big shift here is moving from a "take it all" to a "take what you want" mindset. AI lets you treat a mixed audio track like a box of ingredients, so you can pick out precisely the one you need.
This isn't just a niche tool; it’s part of a massive trend. The AI video market is exploding, projected to grow from USD 3.86 billion in 2024 to USD 42.29 billion by 2033. This boom is what’s making these incredibly powerful audio tools more accessible to everyone. You can see the full research on the AI video market's growth if you want to dig into the data.
Real-World Scenarios for AI Sound Isolation
So, where does this really make a difference? Let's look at a few situations where the old methods just wouldn't cut it.
- For Podcasters: Your remote guest's dog starts barking mid-sentence. Instead of trying to chop around the noise and ruin the flow, you just type "dog barking" to isolate the sound and delete it, leaving your guest’s voice perfectly intact.
- For Musicians: You’ve got a great video of a street performer, but the sound of their acoustic guitar is buried under traffic noise. A prompt like "acoustic guitar melody" can lift the music right out of that chaotic environment.
- For Video Editors: You need to emphasize a key sound in a scene, like the jingle of keys being dropped. By isolating "keys jingling," you can boost its volume in the final mix without making everything else louder.
These examples show how AI gives you a level of creative control that was once reserved for high-end audio engineers. You're no longer stuck with the original mix. If you want to see this in action, our guide on how to extract audio from video online walks you through the process, empowering you to deconstruct and rebuild your soundscapes with incredible precision.
Your Workflow For Precise AI Audio Isolation
Putting theory into practice with an AI tool like Isolate Audio is surprisingly simple. The whole process is designed to be intuitive, swapping out tedious technical steps for a straightforward workflow that anyone can get the hang of.
It all starts with getting your video into the system. The platform is pretty flexible, accepting common video files like MP4 and WebM right off the bat. This means you can drop in footage straight from your camera, a screen recording, or a downloaded clip without having to run it through a converter first.
Crafting Effective Text Prompts
Once your video is uploaded, the AI gets to work based on your text prompts. Getting a great result really boils down to being specific. Sure, a single-word prompt can sometimes do the trick, but a more descriptive phrase gives the AI the context it needs for a much cleaner, more accurate separation.
Think of it like giving directions. "Piano" points to a general location, but "the soft piano melody in the background" is a full itinerary. The more detail, the better.
Here are a few real-world examples to show you what I mean:
Instead of:
vocalsTry:
the lead singer's main vocalInstead of:
carsTry:
the sound of passing trafficInstead of:
birdTry:
a single bird chirping
That extra bit of detail helps the AI pinpoint your target sound and distinguish it from other noise in the mix. This is a game-changer when you need to extract audio from a video file with any kind of precision.
Choosing Your Quality Preset
After nailing your prompt, you'll pick a quality preset. Each one strikes a different balance between processing speed and audio fidelity, so you can tailor the output to what you actually need.
- Best: This is the top-tier option. It uses the most advanced models to capture every detail, making it the go-to for professional projects, music production, or any time audio integrity is non-negotiable. Just be prepared for a longer processing time.
- Balanced: This is the workhorse setting and a great middle ground. You get excellent quality but with a much faster turnaround. I find it’s perfect for most common tasks, like cleaning up dialogue for a social media clip or grabbing a sound effect for a podcast.
- Fast: When you just need a result now, this is your pick. The quality is still surprisingly good, but it's really built for quick previews, rough drafts, or just checking if the isolation is on the right track before committing to a higher-quality render.
This diagram gives you a simple, at-a-glance look at how the core process works.
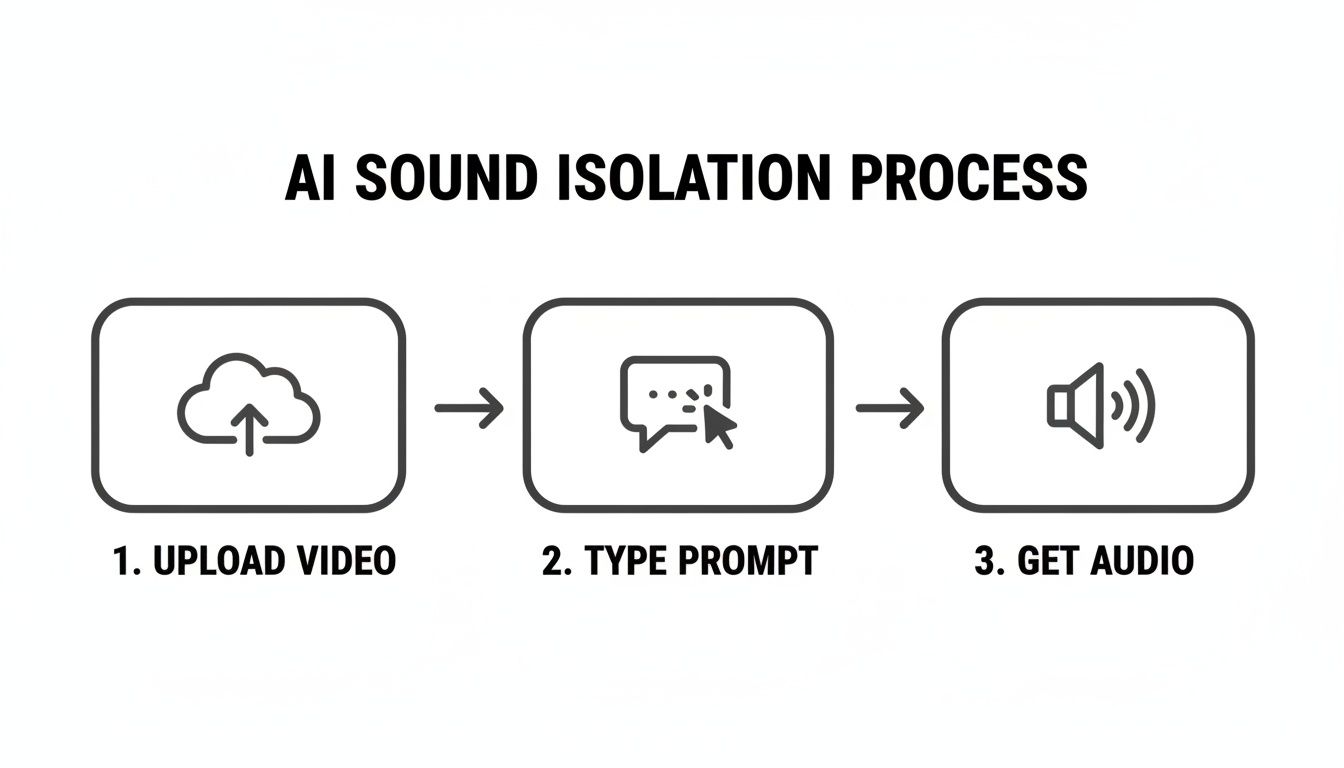
It really shows how you can go from a complex, messy video source to a clean, isolated audio track with just a simple prompt.
Handling Overlapping Sounds With Precision Mode
So, what do you do when two sounds are fighting for the same space? A classic challenge is trying to separate two people talking over each other. This is exactly where Precision Mode comes in handy.
By toggling on Precision Mode, you're telling the AI to dig deeper and perform a more granular analysis of the audio. It helps untangle those overlapping frequencies, making it possible to pull out one specific voice even when another person is speaking at the exact same time.
From my experience, this feature is an absolute lifesaver for cleaning up messy interview audio, editing documentaries, or untangling any chaotic dialogue.
Finally, you’ll pick an output format. If you need the absolute best quality for further editing, go with WAV or FLAC—they're lossless, so you don't lose any data. If file size is a bigger concern for sharing or archiving, a high-quality MP3 is a perfectly good alternative.
Best Practices For High-Quality Audio Results
No matter what tool you reach for to extract audio from a video file, there’s one golden rule: the quality of your source material is everything. The old saying "garbage in, garbage out" is especially true here. A clean, high-resolution video will always give you better audio than a grainy, heavily compressed file you downloaded from a sketchy website.
It's easy to forget that video compression artifacts don't just mess with the visuals—they can bake noise and distortion right into the audio track. So, whenever you can, start with the original, uncompressed video file straight from the camera or recording device. It makes all the difference.
Choose The Right Output Format
With a high-quality source file in hand, your next big decision is the output format. What you choose should depend entirely on what you plan to do with the audio next. This choice is a trade-off between file size and audio fidelity.
For any serious editing, mixing, or professional work, you absolutely want to export to a lossless format.
- WAV: This is the industry standard for uncompressed audio. It gives you the highest possible quality and the most flexibility for editing later on.
- FLAC: This format is also lossless, just like WAV, but it uses clever compression to shrink the file size without sacrificing a single bit of quality. It’s perfect for archiving.
But if you just need to share the audio or get it transcribed, a compressed format is much more practical.
- MP3 (320 kbps): A high-bitrate MP3 strikes a great balance, offering really good quality in a file size that won’t clog up your email.
Think of it this way: WAV is your raw slab of marble, ready for sculpting in the workshop. MP3 is the polished statue, ready for the gallery. You'll always have more creative freedom when you start with the raw material.
This growing need for better audio tools isn't happening in a vacuum. The global audio and video equipment market is on track to hit an incredible USD 362.22 billion by 2030, largely fueled by the creator economy’s endless hunger for professional-grade content. This boom just underscores how vital reliable audio extraction has become for podcasters, YouTubers, and e-learning creators alike.
Post-Extraction Cleanup And Enhancement
Pulling the audio out of a video is often just the beginning. To get that polished, professional sound, you'll probably need to do a little cleanup work. Don't worry, this doesn't have to be a huge production—a few simple tweaks can make a massive difference.
For example, a bit of gentle noise reduction can eliminate that annoying background hum or hiss from an air conditioner without messing with the main audio. If you’re working with dialogue, a subtle EQ boost in the mid-range frequencies can make voices sound clearer and more present. These little adjustments are what separate a raw rip from a truly finished track.
If you’re ready to dive deeper into cleaning up your sound, our guide on how to remove background noise is a great next step.
Common Questions About Audio Extraction
When you first start pulling audio from video files, a few questions always come up. It doesn't matter if you're using old-school software or a new AI tool; getting these basics down can save you a ton of frustration. Let's dig into what creators usually ask.
Can I Isolate Just One Specific Sound?
This is a big one, and the answer really depends on your tools.
Traditional software like VLC or Audacity can't do this. They're built to rip the entire audio track from a video—dialogue, music, sound effects, everything. It all comes out as a single, mixed-down file.
If you need to grab just a single sound, like a dog's bark or a specific line of dialogue without the background music, you need something smarter. This is where an AI tool like Isolate Audio shines. You can feed it your video and simply type in a prompt like "dog barking." The AI then separates that specific sound for you, giving you a clean track with just the sound you wanted.
What Is The Best Audio Format After Extraction?
There's no single "best" format—it all comes down to what you're doing with the audio next. Picking the right one from the start is key.
- For Editing and Professional Work: Go with a lossless format every time. Think WAV or FLAC. These formats are uncompressed, meaning they keep every bit of the original audio data. This gives you the highest possible quality for mixing, adding effects, or any other detailed work.
- For Sharing and General Use: A high-quality MP3, like one encoded at 320kbps, is usually your best bet. It strikes a fantastic balance between decent sound quality and a much smaller file size, which is perfect for emailing, uploading to the web, or running through a transcription service.
Is It Legal To Extract Audio From Any Video?
This is where you need to be careful, because it all comes down to copyright.
If you're pulling audio from a video you created yourself, you're golden. It's your content, and you can do whatever you want with it.
The trouble starts when you extract audio from copyrighted material you don't own—like a blockbuster movie, a TV show, or a popular song. Using that audio for your own public or commercial projects without getting permission is a fast track to copyright infringement. While there are some grey areas for personal use or "transformative" works, the safest route is to always be cautious with other people's content.
Do Online Converters Reduce Audio Quality?
Most of them do, yes. Many free online converters prioritize speed and low server costs over quality. To make that happen, they often use aggressive compression that can strip out the subtle details and frequencies from your audio. You might end up with a file that sounds flat, tinny, or has noticeable artifacts.
If sound quality is a priority for your project, it's always better to use dedicated desktop software or a professional service that offers high-quality, lossless output. That's the only way to be sure the audio you end up with is as clean and clear as the original source.
Ready to move beyond just ripping the whole track? Isolate Audio uses AI to understand what you're looking for and pulls specific sounds directly from your videos based on simple text prompts. Try it for free today at https://isolate.audio.